You have a workbook with 12 worksheets, 1 for each month. All of the worksheets have the same number of rows and columns. You want a summary worksheet in order to total January through December.
To create it, use the formula =SUM(January:December!B4).
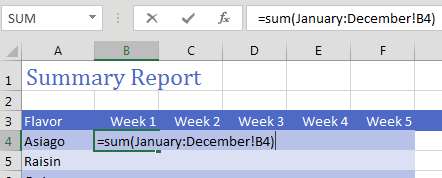
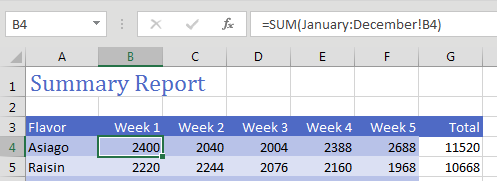
Copy the formula to all cells and you will have a summary of the other 12 worksheets.
Caution
I make sure to never put spaces in my worksheet names. If you do use spaces, the formula would have to include apostrophes, like this: =SUM('Jan 2018:Mar 2018'!B4).
Comments
Post a Comment