Power Query cleans and transforms data
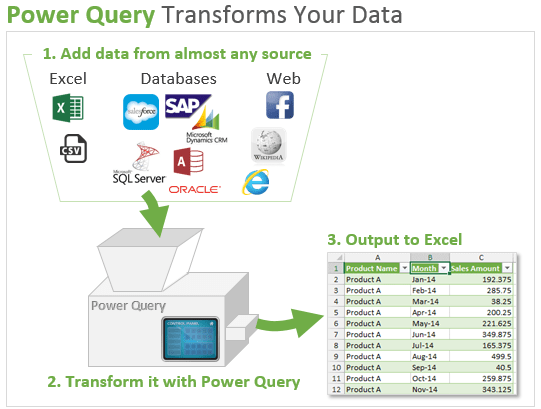
- You add your data sources (Excel tables, CSV files, database tables, webpages, etc.)
- Press buttons in the Power Query Editor window to transform your data.
- Output that data to your worksheet or data model (PowerPivot) that is ready for pivot tables or reporting.
Power Query is like a machine because once you have your query setup, the process can be repeated with the click of a button (refresh) every time your data changes.
If you have used macros to transform your data, you can think of this as a much easier alternative to VBA that does NOT require coding.
Common Data Tasks Made Easy
Do you work with data that has been exported from a system of record? This could be a general ledger, accounting, ERP, CRM, Salesforce.com, or any reporting system that contains data.
If so, you probably spend a lot of time transforming or re-shaping your data to create additional reports, pivot tables, or charts.
These data transformations could include tasks like:
- Remove columns, rows, blanks
- Convert data types – text, numbers, dates
- Split or merge columns
- Sort & filter columns
- Add calculated columns
- Aggregate or summarize data
- Find & replace text
- Unpivot data to use for pivot tables
Do any of these tasks sound familiar? If so, then they probably also sound boring, repetitive, and time consuming. 🙂 Believe me, I’ve spent the better part of my career doing these tasks and trying to figure out faster ways to get them done.
Fortunately, Power Query has buttons that automate all these tasks!
Overview of the Power Query Ribbon
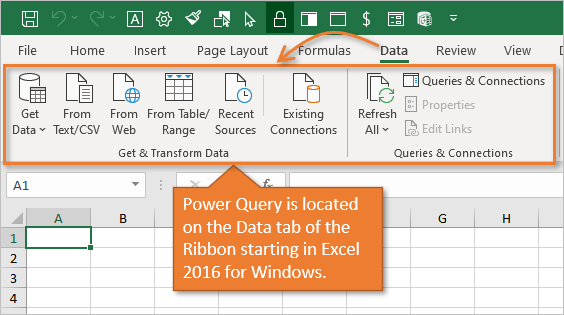
Starting in Excel 2016 for Windows, Power Query has been fully integrated into Excel. It is now on the Data tab of the Ribbon in the Get & Transform group.
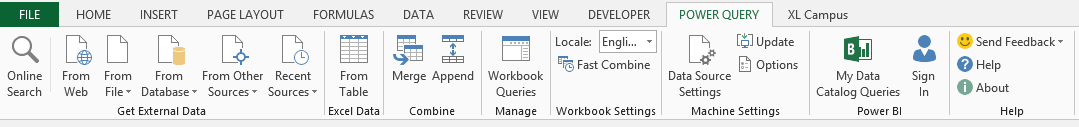
In Excel 2010 and 2013 for Windows, Power Query is a free add-in. Once installed, the Power Query tab will be visible in the Excel Ribbon.
You use the buttons in the Data or Power Query tab to get your source data. Again, your data could be stored in Excel files, csv files, Access, SQL server database, SharePoint, Salesforce.com, Dynamics CRM, Facebook, Wikipedia, websites, and more.
Once you have specified where your data is coming from, you then use the Power Query Editor window to make transformations to the data.
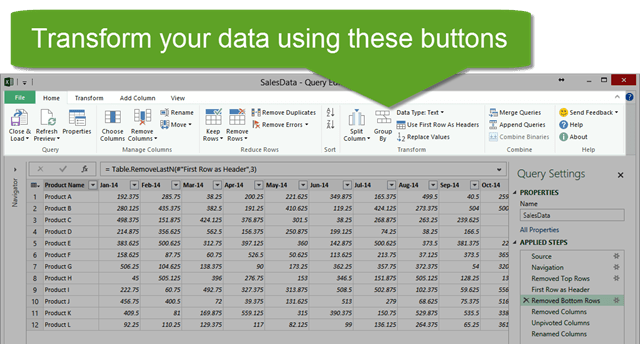
The buttons in the Power Query Editor Window allow you to transform your data.
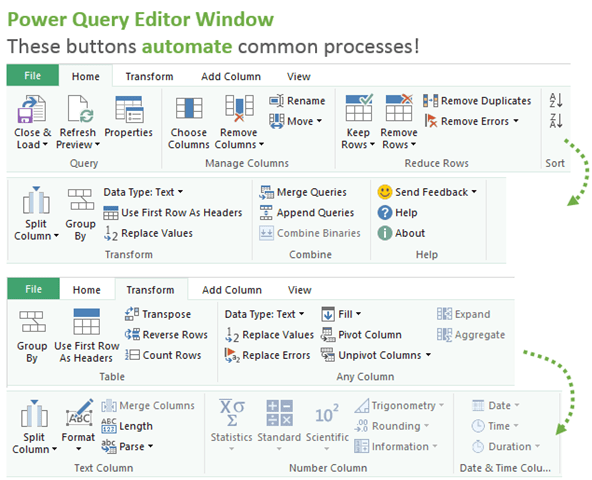
Think about some of those tasks you do repeatedly as you browse the buttons in the image above. Each time you press a button your actions (steps) are recorded, and you can quickly re-apply the steps when you receive new data by refreshing the query.
After completing your steps, you can output the data to a Table in your Excel workbook by clicking the Close & Load button.
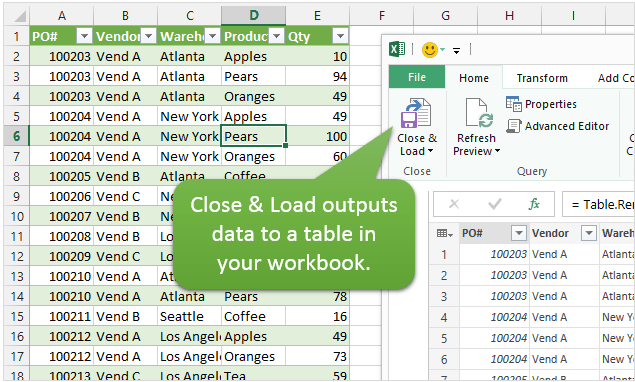
You can also modify existing queries and refresh your output tables with the changes or updated data.
Data Transformation Examples
Here are a few examples of what Power Query can do with your data.
Unpivot Data for Pivot Tables
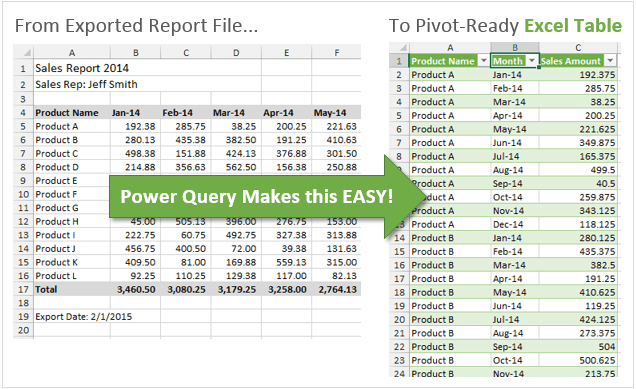
My favorite feature of Power Query is it’s ability to Unpivot data. This is a technique used to get your data ready for the source of a pivot table. This is also referred to as normalizing your data to get it in a tabular format.
The data might start out looking something like the following.
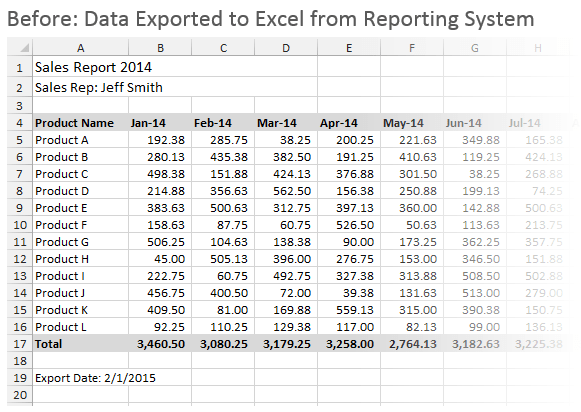
And you want the end result to look like this.
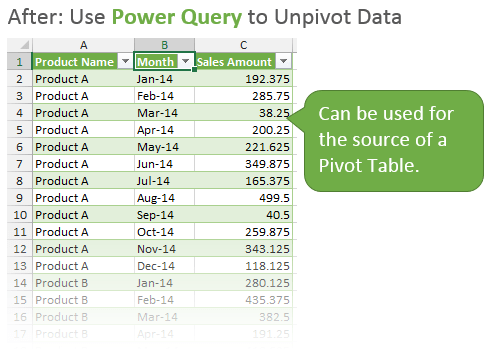
Power Query can do this with the click of a few buttons, and prepare your data for use in a pivot table.
Comments
Post a Comment