Formatting In Excel - helps you find meaning in the spreadsheet
Spreadsheets are often seen as boring and pure tools of utility, but that doesn't mean that we can't bring some style and formatting to our spreadsheets
Formatting helps your user find meaning in the spreadsheet without going through each and every individual cell. Cells with formatting will draw the viewer's attention to the important cells.
In Excel, formatting worksheet data is easy. You can use several fast and simple ways to create professional-looking worksheets that display your data effectively. For example, you can use document themes for a uniform look throughout all of your Excel spreadsheets, styles to apply predefined formats, and other manual formatting features to highlight important data.
Formatting a Data
Raw Data
Using Font, Number tabs as shown in image to do a simple formatting
Formatting a Data with help of formatting tools in Excel
As shown in image , we have Product category wise data with Taxable value, Cost, Profit and Profit Ratio.
There are no gridlines, headers, formula bar and ribbon, these can be hidden with formatting tools.
In Below Image you can see Formula tab, header and gridlines
Below is a Report prepared using various formatting tools like chart and Smart Art.
As shown above we can convert a simple data into a nice and presentable form with the help of formatting tools available in Excel.
As shown in image below, with this style of formatting and presenting a data there is no need to rework the data and show it in PowerPoint.
Types of Formatting
Press Ctrl +1 or
1. Numeric
I. Date formatting
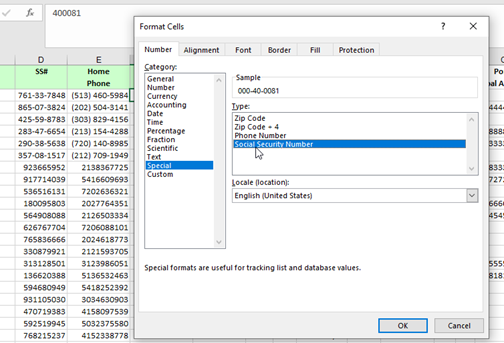
II. Special Formatting – Change Security code number formatting and Phone number formatting.
III. Custom Formatting
You can custom a formatting as required
2. Display
In Home Tab – Font feature
Change font of the text , size, Colour
Fill colours in cell
Apply borders
Underline, Bold or Italic a character
3. Tools
Justify option allows the text copied from internet or word to be changed.
Background – Change background from Page layout option
4. Row & Column
Data with no Row or column formatting
After adjusting row and column
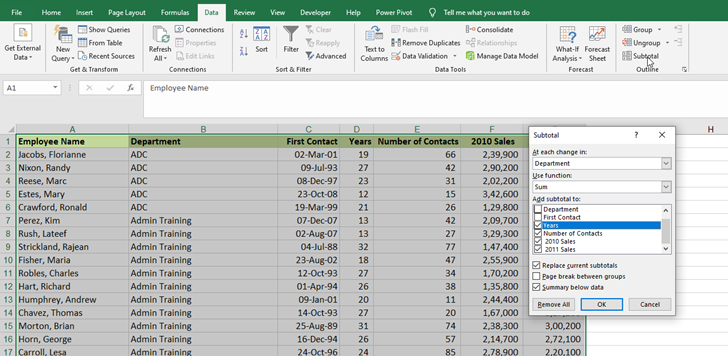
5. Outlining
Data Tab – Outline -- Subtotal
After Outline
Grouping
Data Tab – Outline -- Group
6. Visualization
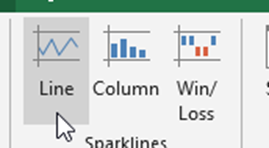
Sparklines – Insert High, Low, first, last, negative markers.
WordArt
Shape Effects
Themes
Pagelayout – Colours or Themes
7. Conditional
Home – Conditional Formatting – there are various options for formatting as shown in image.
Conditional Formatting with Formula



















Comments
Post a Comment