There are two consolidation tools in Excel.
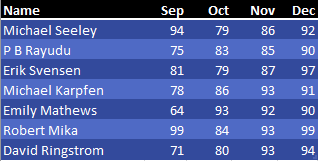
You have three data sets. Each has names down the left side and months across the top. Notice that the names are different, and each data set has a different number of months.
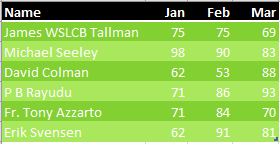
Data set 2 has five months instead of 3 across the top. Some people are missing and others are added.
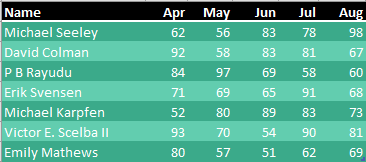
Data set 3 has four months across the top and a few new names.
The Consolidate command will join data from all three worksheets in to one worksheet.
You want to combine these into a single data set.
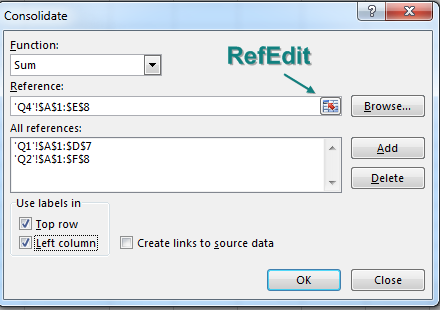
The first tool is the Consolidate command on the Data tab. Choose a blank section of the workbook before starting the command. Use the RefEdit button to point to each of your data sets and then click Add. In the lower left, choose Top Row and Left Column.
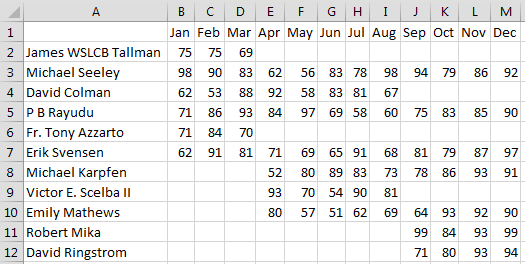
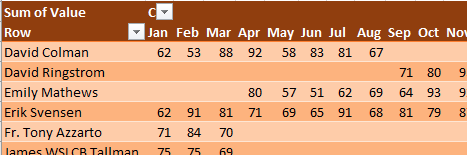
In the above figure, notice three annoyances: Cell A1 is always left blank, the data in A is not sorted, and if a person was missing from a data set, then cells are left empty instead of being filled with 0.
Filling in cell A1 is easy enough. Sorting by name involves using Flash Fill to get the last name in column N. Here is how to fill blank cells with 0:
- Select all of the cells that should have numbers: B2:M11.
- Press Ctrl+H to display Find & Replace.
- Leave the Find What box empty, and type a zero in the Replace With: box.
- Click Replace All.
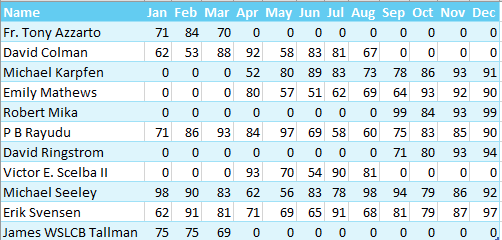
The result: a nicely formatted summary report, as shown below.
The other ancient tool is the Multiple Consolidation Range pivot table. Follow these steps to use it:
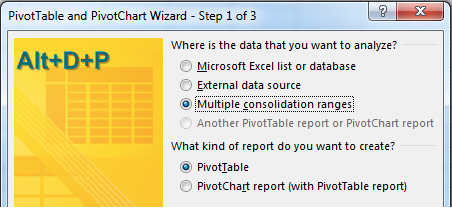
1. Press Alt+D, P to invoke the Excel 2003 Pivot Table and Pivot Chart Wizard.
2. Choose Multiple Consolidation Ranges in step 1 of the wizard. Click Next.
3. Choose I Will Create the Page Fields in step 2a of the wizard. Click Next.
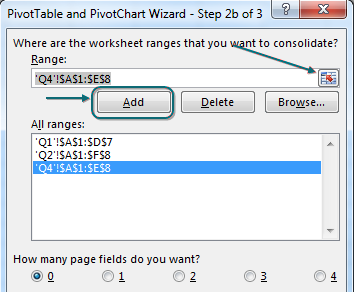
4. In Step 2b of the wizard, use the RefEdit button to point to each table. Click Add after each.
5. Click Finish to create the pivot table, as shown below.
Comments
Post a Comment