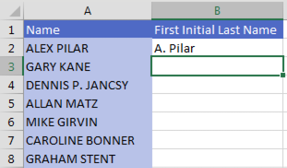
Type the first initial in B3. Excel sees what you are doing and “grays in” a suggested result.
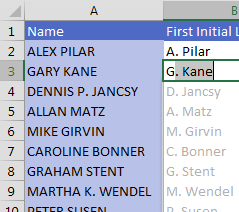
Press Enter to accept the suggestion. Bam! All of the data is filled in.
Look carefully through your data for exceptions to the rule. Two people here have middle initials listed. Do you want the middle initials to appear? If so, correct the suggestion for Dennis P. Jancsy in cell B4. Flash Fill will jump into action and fix Martha K. Wendel in B9 and any others that match the new pattern. The status bar will indicate how many changes were made.
In the above case, Excel gurus could figure out the formula. But Flash Fill is easier. In the example shown below, it would be harder to write a formula to get the last word from a phrase that has a different number of words and more than one hyphen.
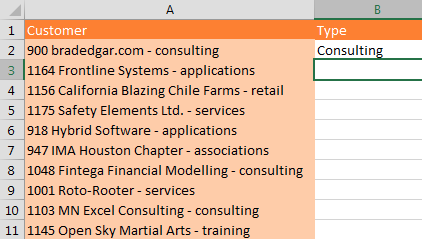
Flash Fill makes this easy. Go to cell B3 and press Ctrl+E to invoke Flash Fill.

Note
Flash Fill will not automatically fill in numbers. If you have numbers, you might see Flash Fill temporarily “gray in” a suggestion but then withdraw it. This is your signal to press Ctrl+E to give Flash Fill permission to fill in numbers.
This comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
ReplyDelete