Sometimes, you want to see many different results from various combinations of inputs. Provided that you have only two input cells to change, the Data Table feature will do a sensitivity analysis.
Using the loan payment example, say that you want to calculate the price for a variety of principal balances and for a variety of terms.
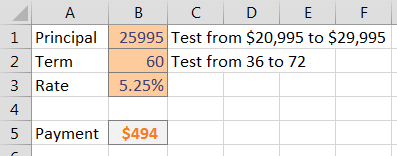
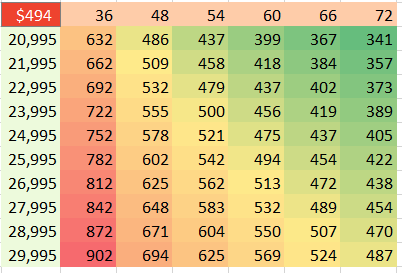
Make sure that the formula you want to model is in the top-left corner of a range. Put various values for one variable down the left column and various values for another variable across the top.
From the Data tab, select What-If Analysis, Data Table....
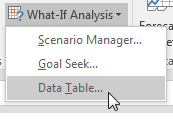
You have values along the top row of the input table. You want Excel to plug those values into a certain input cell. Specify that input cell for Row Input Cell.
You have values along the left column. You want those plugged into another input cell. Specify that cell for the Column Input Cell.
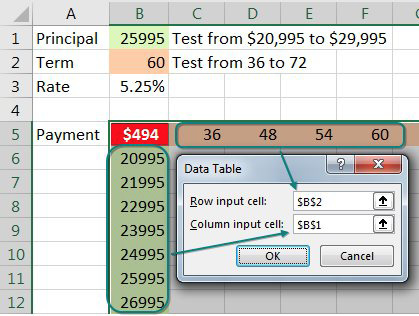
When you click OK, Excel repeats the formula in the top-left column for all combinations of the top row and left column. In the image below, you see 60 different loan payments, based on various inputs.
Note
I formatted the table results to have no decimals and used Home, Conditional Formatting, Color Scale to add the red/yellow/green shading.
Here is the great part: This table is “live.” If you change the input cells along the left column or top row, the values in the table recalculate. Below, the values along the left are focused on the 23K to 24K range.
Comments
Post a Comment