In the figure below, say that you want to find any changes between column A and column D.
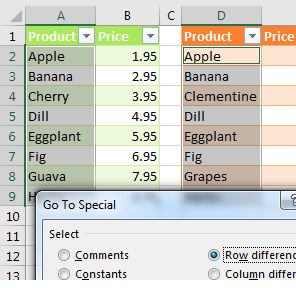
Select the data in A2:A9 and then hold down the Ctrl key while you select the data in D2:D9.
Select, Home, Find & Select, Go To Special. Then, in the Go To Special dialog, choose Row Differences. Click OK.
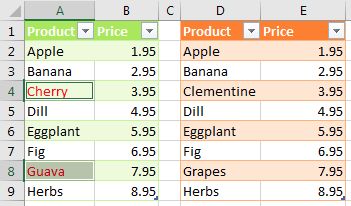
Only the items in column A that do not match the items in column D are selected. Use a red font to mark these items, as shown below.
Caution
This technique works only for lists that are mostly identical. If you insert one new row near the top of the second list, causing all future rows to be offset by one row, each of those rows is marked as a row difference
Comments
Post a Comment